Fast Facts About Gout
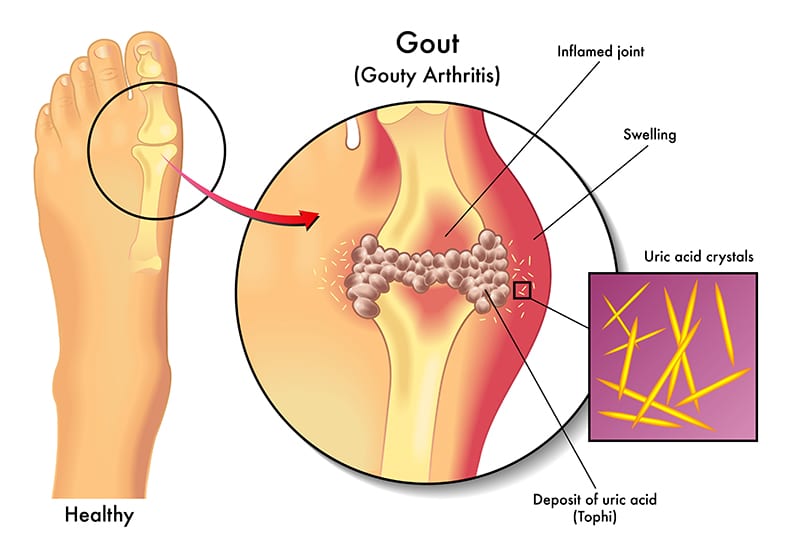
Gout present in the big toe is known as podagra and is characterized by the reoccurring attacks of inflammatory arthritis-hot, red , swollen joint. Pain comes after every 12 hours and joint at the big toe is affected in most cases. This can result in kidney stone, urate nephropathy or tophi. Genetic factors combined with diet is the major cause of gout. People who eat a lot of meat and beer are mostly affected. Obesity can also lead to gout. Elevated levels of uric acid will be present in these mechanisms. During an attack, blood uric acids will be normal.
Treatment with NSAIDs, colchicine or steroids can improve the symptoms. Levels of the uric acid can be lowered by changes in lifestyle once the acute attack subsides. Probenecid or allopurinol can provide long-term prevention in these frequent attacks. Those who suffer from gout must have food rich in vitamin C and should also consume very little of the dairy products.
Symptoms and Signs:
As mentioned earlier, the most common way in which gout can be present is a recurring attack of inflammatory arthritis. The toe is mostly probably affected but other areas like knees, heels, fingers and wrists can also be affected. Pain occurs in 2-4 hours and generally at night and depends on the body temperature. High fever and fatigue are other symptoms observed on a person being affected by gout.
Cause:
The main cause of gout is the crystallization of uric acid with high levels in the blood. This happens due to the salts of uric acid, diet, underexcretion of urate and genetic predisposition.
• Lifestyle- 12% of gout is caused due to the diet. This includes the consumption of fructose- sweetened drinks, seafood, meat, and alcohol. It is always better to consume coffee and foods rich in vitamin C.
• Genetics- 60% of the variability in the uric acid is through genes. Three genes called SLC22A12, ABCG2, and SLC2A9reduce urate absorption and urate secretion.
• Medication- Medicines like aspirin and niacin increase the risk of the attack of gout.
Diagnosis:
With classic podagra and hyperuricemia, gout can be diagnosed and treated without any further investigations. Synovial fluid analysis is a good way to diagnose gout if there is any doubt in the previous methods. X-rays are also used in diagnosing but they have a small utility in acute attacks.
Prevention:
Medications and changes in the lifestyle can decrease the levels of uric acid. Reduce the intake of alcohol, seafood, and meat and consume foods rich in Vitamin C. Obese men should have foods low in calorie and this would gradually decrease the levels of uric acid in the blood by 100 micromol/L. 1500mg of vitamin C daily would decrease the risk of gout by 45%. Instead of tea, have coffee to reduce the risk of gout.
Treatment:
Settling the symptoms of an acute attack is the initial aim of treatment. Different types of drugs are used to prevent repeated attacks and will subsequently reduce the levels of serum uric acid.








